The term civilization is understood as the culmination of knowledge and wisdom, which are common to a group of human beings in a period of time. If we add the word “ancient” to the definition, these characteristics are transported to a specific moment in history. In this way, many civilizations have been created, each one contributing its own knowledge and customs, in order to create a civilization or society with great historical importance. In this article, we will investigate how the first civilizations were formed, which ones were the most important, what they contributed to society, etc. It is time to learn more about ancient civilizations.

When we talk about a “civilization” we are talking about a society that has developed to a high standard not only its economy but also its political, cultural and religious organization. Civilization is the highest degree of development that a society can achieve.
Ancient civilizations were formed thousands of years ago, but they have been the fundamental basis for the social advancement that we have today in the 21st century, which stands out for being the technological age. If it hadn’t been for the first civilizations, with their inventions, writing, and trade, as well as their political structures, we wouldn’t have the same level of evolution that we take for granted in today’s social structure.
Ancient Civilizations
Contents
- Ancient Civilizations
- Ancient Civilizations: Society
- Ancient Civilizations: State Organization
- Ancient Civilizations: East
- Ancient Civilizations: East – The Sumerians
- Ancient Civilizations: East – The Akkadians
- Ancient Civilizations: East – Mesopotamia
- Ancient Civilizations: East – Ancient Egypt
- Ancient Civilizations: Europe and the Mediterranean
- Ancient Civilizations: Europe and the Mediterranean – Ancient Greece
- Ancient Civilizations: Europe and the Mediterranean – The Roman Empire
- Civilizations Today
It can be said that the development of all these civilizations coincides in certain points, in which each society has had to progress in order to adapt and above all survive.
All civilizations arise around rivers, which are considered a focal point. Rivers were a source of water, essential for the development of agriculture, aside from being an important way of transporting merchandise. The rivers ensured that food would be available, offering an abundance of fish, a fundamental food for emerging civilizations, in addition to preserving the health of the group, offering the ideal medium for cleaning and personal hygiene.
A group is considered to be a civilization when they are capable of using and working with metals both for daily use and for defense, when they have a state or political organization that can be considered fairly professional, and when they are able to distribute different jobs, even creating specializations within the job. They are also societies who are able to produce enough in order to be self-sufficient, with a distinctive style of art and who hold some common beliefs.

Elements of Civilizations
We find two characteristic elements within a civilization. The first is essential, the other is complementary, they are derived from the first and have now become inseparable.
I). Essential.- Here we find human sociability and religion. Many authors indicate that the essential elements are the same as the cultural factors of a civilization. But to avoid confusion, we have decided to name them “essential factors”.
- a) Human sociability. – Within human sociability, there are two driving factors: family and language. Both are a product of man’s need to socialize, and both allow the continued existence of the civilization. The family is the first source that the new members of society are exposed to, receiving their parents’ habits (a phenomenon known as enculturation) and language is the medium through which civilization is spread, through oral traditions.
- b) Religion – this could also be seen as an ideological element in a more general way. Humans tend to group up with the people who share the same beliefs as them. An example of this is the Muslim civilization, united by their God Allah. Or the Western civilization which identifies itself as being Catholic or Protestant, both of which stem from Christianity.
(II). Complementary Elements.These are the most abundant elements; according to some authors, up to 7 elements can be included. These elements allow the subsistence of the first and even of their own development and expansion to other groups. These elements also determine the process of growth within the civilization itself. If the first give their characteristics and uniqueness with regards to other civilizations, these elements determine the characteristics.
We can mention the following:
- The accumulation of wealth, which depends on the type of work. This should generate surplus production to ensure the development of science and technology and thus the growth of the civilization.
- Physical agents such as climate, soil, the geographical aspect in general, nature and man himself. Perhaps man should not be here, but by his material constitution, this is taken into account.
- Trade, as it allows communication between one village and another, thus enabling their cultural enrichment.
- Art, because it causes emotions in human beings, and is also a reflection of our aesthetic and evaluative side.
- Instruction or teaching, as it is necessary for people to know their own history, as well as being trained in the use of techniques and theories.
- Inventions and applications, which save time and effort in the production process.
- And lastly, although it is not considered an important or determining factor, but rather a simple consequence of civilization, we refer to the management of the government.
It may be seen that these elements are of a pro-capitalist nature. People unconsciously defend the permanence of a mode of production, as that is where their food source comes from.

Ancient Civilizations: Adaptation to the Environment
A civilization implies an effective adaptation to their environment, as it needs to feed a huge population. This adaptation can be achieved through slash-and-burn agriculture (like the Mayas) or intensive agriculture (Egypt, Incas, Aztecs, etc). According to the particular characteristics of the environment in which each civilization has developed, different techniques are used to make the most of the harvests and overcome the natural obstacles of each region.
In Egypt and Mesopotamia they constructed canals and irrigation works;
the Aztecs built ponds of fertile earth called Chinampas in order to benefit from the extensive lake Texcoco.
The Incas made “cultivation terraces” in the Andes mountain range so they could have flat lands suitable for agriculture.
Ancient Civilizations: Society
Given that their main economic activity was agriculture, the vast majority of the population devoted themselves to agricultural tasks. But as these societies increased in size, their necessities also began to grow. The first specialized groups in various arts began to appear, whose formation based on experience began to pass from parents to children, creating trade groups such as administrators, military, priests, masons, craftsmen, officials, architects, etc.
There is a clear division between the city or the ceremonial center (urban) and the countryside (rural). The most relevant and important buildings were the buildings used by the Government, institutions, palaces, temples, assembly points, etc., made up the city or ceremonial center and place of residence of the craftwork and military classes, etc. ultimately all of those who directly depended on the city. The peasants, however, were relegated to the rural areas, in the countryside.

In Ancient History, we find that civilizations show a clear social stratification. By social stratification, we understand that the dominant group of society (nobility), through the control of the State, enforced the rest of the population to pay a tribute. A tribute is a tax that the inhabitants pay to the state, in products, as well as in work or money.
Ancient Civilizations: State Organization
Civilization is politically governed under the supervision of the State. The term “State” is understood as the existence of a centralized power, with a permanent army, and organization and control of its territory. Thanks to this centralization of power, the State has the ability to govern a population by imposing the payment of tributes and the obligation to carry out certain tasks for the benefit of society (army, public works, farming state land etc).
Within the head of State, a dominant group can be found that can control the resources received as tributes and redistribute them according to the group’s needs (for example, to reward prominent officials or soldiers, or to help people who have lost their harvests).
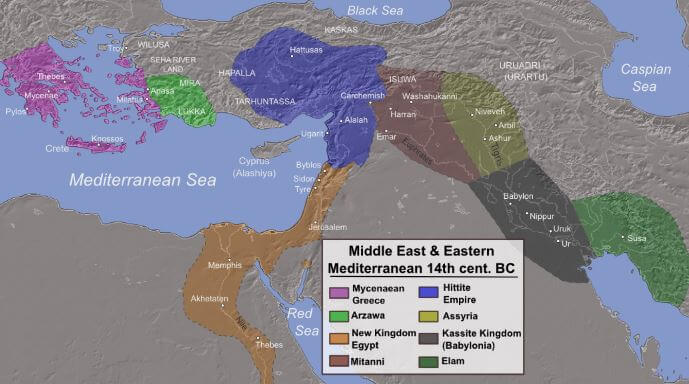
Ancient Civilizations: East
The first organized groups that we can call civilizations developed in the East, where their influence over other – perhaps more incipient – cultures, unavoidably contributed to the formation of what we now call Western Culture.
Civilizations as the Mesopotamian, Egyptian, Phoenician, and Hebrew, inhabited the furthest corners of the East, developing activities such as trading, in which the Phoenicians particularly stood out, while on a spiritual level the Hebrews provided the basis of the majority of future religions.
3000 years ago the East was already inhabited and even organized; different cultures and peoples lived in this region, where life revolved mainly around agricultural activities.
Ancient Civilizations: East – The Sumerians
The Sumerians are the oldest civilization in the world, they were settled in Mesopotamia. The origin of this civilization is unknown, but it is known that they lived approximately 5500 years ago. We know a lot about this civilization thanks to the depictions that they have left us through their artistic creations.
The Sumerians were mainly farmers and ranchers and must have had basic engineering knowledge as they were able to build canals and roads, they sailed, fashioned fabrics with wool and were able to make tools, as they knew how to work with metals.
Their Contributions
One of the contributions that the Sumerians left for mankind was the invention of Cuneiform writing, which has much relevance today as it allowed them to broadcast events and thoughts that have survived until today.
Ancient Civilizations: East – The Akkadians
The Sumerians and the Akkadians came to live together as neighbors, the Akkadians in the north of Mesopotamia and the Sumerians in the south. The Akkadians invaded the Sumerians, therefore unifying Mesopotamia.
The Akkadians forced the conquered Sumerians to learn their language, leading the Sumerian language to practically disappear, reducing knowledge only to the priests, as they could only carry out their liturgy in the Sumerian language.
Their Contributions
Cities such as Babylon showed the splendor of an advanced and organized civilization, with very advanced artistic, architectural, hydraulic, medical and legislative contributions, capable of organizing almost unbeatable armies. The emergence of the Hammurabi code allowed us to reveal their political and social organization, the laws that governed society and the penalties for failing to meet them. Mathematical calculations advanced enough to build large infrastructures were also discovered.
Ancient Civilizations: East – Mesopotamia
An example of the importance that rivers had in ancient civilizations can be found in Mesopotamia, whose name means “between rivers”. A culture settled between the rivers Euphrates and Tigris, two of the most important rivers of the Near East, which also brought all the nutrients needed in order for the society to secure its highly important agricultural production.
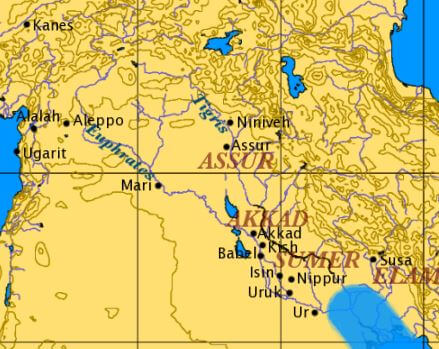
Mesopotamia has suffered throughout all of its history from invasions by other cultures who longed to steal the riches of their land. So many struggles and invasions interrupted this ancient civilization’s development, giving way to other peoples who also settled in these territories such as the Sumerians, the Babylonians, and the Syrians.
Mesopotamian civilization was composed of different political organizations, such as the famous empires of Sumer, Akkad, and Assyria, amongst others, but the different territories that it constituted of shared some common beliefs and customs.
The Mesopotamian civilization survived until the 1st century B.C. when the territory where it was located was conquered in the year 539 B.C. by the Achaemenid Empire and then in 332 B.C. by Alexander The Great. It is thought that writing was born in the Mesopotamia around the year 3100 B.C., thus opening the metaphorical doors to this historical period.
It was precisely in Mesopotamia where the first large libraries were created and where what can be considered as the first books known to humanity were found. Some of them are still preserved, such as the famous poem of Gilgamesh, where the adventures of a King in search for immortality are told, and also where some of the first descriptions of the Great Flood can be found. Furthermore, Mesopotamian civilization also experienced a major breakthrough in the field of mathematics, introducing a numerical system of a sexagesimal base. The database was particularly useful when it comes to measuring time, as it is based on the segmentation of one hour in cycles of 60 minutes, the division of the days in periods of 24 hours and also the calculation of the 360º of the circle.
Closely linked with mathematics and religion was their development of the art of astronomy. Mesopotamian astronomers, especially those related to the Babylonian Empire, accurately calculated eclipses and solstices and were the first to divide the year into twelve months, splitting it into two seasons, summer and winter.
Finally, they made very important progress in the technological and architectural fields that are still used today. Techniques that they used in the agricultural sector, gardening and in the creation of beautiful gardens are particularly relevant.
They invented advanced irrigation techniques to control the flow of the water from the two rivers that their name comes from, water accumulation and to extract metals as the iron, bronze, and copper.
Impressive palaces were decorated with complex techniques such as glazed brick and they also created huge monumental structures such as the magnificent gates of Ishtar which can be found in the Pergamon Museum in Berlin or the huge Ziggurats that even today, thousands of years after its construction, can still be seen in various areas of the current Middle East.
Ancient Civilizations: East – Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt is one of the history’s most fascinating civilizations, because of everything that is already known about them and also all the things that are overlooked. This civilization emerged around 5000 years ago when the towns and settlements that stood on the banks of the Nile began to gather and form part of a “whole”.

Many things from Ancient Egypt are still with us today, such as the pyramids where they buried their Pharaohs, or their hieroglyphs, their curious way of writing. We also know that they cultivated plants on the wet land on the banks of the Nile, they had reservoirs to remove stones and metals and that they were great traders.
One of the fascinating aspects of the Egyptians, apart from having a mythology full of Gods, legends, and tales of the afterlife, is the proficiency they seemed to have at mathematics. Some of the discoveries that have been made regarding their command of numbers and arithmetic are astonishing.
The end of the Ancient Egyptian civilization is marked by the invasion of the Roman Empire, around the 4th century B.C. which means that the glory of their reign lasted for around 2500 years.
Ancient Civilizations: Europe and the Mediterranean
In Europe, the most important civilizations also emerged around rivers or oceans. The trade routes of the East had such a strong influence that whilst the ancient civilizations of the East were forming, they caused the ancient civilizations of the West to evolve almost simultaneously.
Ancient Civilizations: Europe and the Mediterranean – Ancient Greece
The heyday of the Ancient Greeks lasted approximately a millennium since they came out of the Dark Ages in the year 1200 B.C. until the Greeks were conquered, unsurprisingly, by the Roman Empire in the 2nd century B.C.
In Ancient Greek civilization, major developments were made in various fields such as philosophy, mathematics, logic, astronomy, and so on. In addition, they developed a political system called democracy. The ancient Greek population lived in Polis, which were something like today’s independent cities.
In spite of belonging to the same empire, each section of Ancient Greece had its own Government. For example, in Athens democracy prevailed and most of the population learned arts or crafts. Meanwhile, Sparta was governed by Kings and their inhabitants were trained to become soldiers.
Ancient Civilizations: Europe and the Mediterranean – The Roman Empire
The Ancient Roman Empire was one of the most extensive empires that have existed on the face of the Earth. Its influence has been felt throughout centuries of history and many countries still have ample evidence in the form of monuments and buildings which date back to that period.
Unlike the Greeks, who stood out on an intellectual and theoretical level, the Roman Empire stood out for more practical reasons (one can see that their Gods and beliefs were copied from the Greeks; they simply changed the names). One of their biggest contributions were their major engineering works: roads, bridges, aqueducts, baths and much more.
The Roman Empire was also the birthplace of Christianity and of civil law. Their leading figure was the Emperor, who possessed an almost omnipotent power. The Emperor’s position was a life-long one, which is why plots and treasons to remove them from their position were very frequent.
The public shows that their high nobles enjoyed were notorious, such as gladiator fights or chariot races. Rome had a destructive military power, but also a great instability which was only stopped for 40 years with the so-called Pax Roma.
The end of the Roman Empire arrived in the 5th century when the Heruli deposed the last of the Emperors, Romulus Augustus.
Civilizations Today

In current times, we can list the following civilizations:
a) China. – Its existence goes back to 1500 B.C. some consider it Confucian, as he was the philosopher who mostly shaped the Chinese people’s ethics. It also takes its name from the Sinic civilization.
b) Japan. – Many consider it to be part of Chinese culture, however, this is far from true because the Japanese maintain distinctive features. Its beginning dates back to the year 100 to 400 B.C.
c) Hindu – or Hindustani. This cannot be confused with China because they have different religious elements. In India, the figure of Buddha prevails and religion is ascetic. Although several streams of Hinduism have arisen, the essence remains the same. In India today other religions also have survived, such as Islam and Confucianism.
d) Islamic. – Emerged in the Arabian peninsula in the 7th century A.D., spread rapidly by North Africa and the Iberian peninsula. United by a single religion, though there are several different versions of Islam: Arabic, Turkish, Persian, and Malaysian.
e) Orthodox. – Originating from Russia. Although they have an origin in common with the West, they followed different paths. The Orthodox community also received the influence of Tatars, despotism and the limited influences received from the Renaissance.
f) Western. – It is generally thought that it began around 700 or 800 A.D. It has three centers: Europe, North America, and Latin America.
g) Latin American. – This is a much-discussed subject. Some consider it as part of Western culture, but others prefer to consider it separately. On a religious basis, it is generally said that the West has been principally Catholic and Protestant, while Latin America has always been Catholic, although that trend is changing lately. Also, in Latin America, Western culture has undergone fusion with indigenous cultures as the Andean, which gives it its own essence.
The Life Cycles of Civilization
The largest human organizations have components that are essentially identical, and which characterize them as such. Indeed, the identical elements are actually the men and women that form it, which is why it is more appropriate to speak of vital processes and types of relations that are essentially equal, and of products or fruits which are multiple and varied. The five vital stages of expression are the same as any human being: birth, growth, peak, decline and death. A system grinds to a halt when it ceases to perform the functions for which it was originally created. A political and social system grinds to a halt when it stops serving its people, and isolates itself in a metaphorical pole, rejecting or refusing the increasingly evident existence of the other pole.
Although civilizations remain, they also evolve. They are dynamic, they grow and collapse; they merge and divide; and as any history student knows, they also disappear and become buried in the oblivion of time.
According to Quigley, civilizations pass through seven stages: mixing, gestation, expansion, conflict, universal empire, decadence, and invasion.
Toynbee thinks that a civilization arises as a reaction to certain stimuli, and after undergoing a period of growth that implies an increase of control over their environment produced by a creative minority, this period will be followed by times of difficulties, the birth of a universal state and an eventual collapse.
This concludes this post on the development of civilization and ancient societies. Keep reading this website to learn more about ancient civilizations.
