There is no doubt that ancient civilizations made significant and important contributions in all fields of life for humankind. These contributions allowed humans to develop and function better in their daily lives; thus societies managed to make big leaps in their economic and political development, as well as cultural production and their religion, whilst simultaneously leaving a legacy in evolutionary history for future generations. This consequently causes specialization and modernization, which eases such operations even more. Below is a list of some of these contributions.
Ancient Civilizations Contributions
Contents
- Ancient Civilizations Contributions
- Contributions made to mankind by the Egyptian civilization
- Contributions made by the Mesopotamian culture
- Contributions made by the Indian Civilization
- Math
- Contributions made by the Chinese Civilization
- Cultural contributions of the Greek civilization
- Contributions made by the Roman Civilization
- Contributions made by the Aztec Civilization
- Contributions made by the Mayan Civilization
Contributions made to mankind by the Egyptian civilization
The Ancient Egyptians made huge contributions to mankind, which were essential for the development of society. Some examples include their problem-solving techniques, their vision and ways of seeing the world, which subsequently served humankind to create thought and reasoning in general, ways of recording history, and many other things, which are mentioned below:
Hieroglyphics

This is a way of writing, which derives from Greek, “heiros” meaning sacred and “glypho” which means sculpt, etc. They were mainly pictograms, which symbolized people, animals, plants, and stylized objects, which were inscribed on Papyrus, temples, and pyramids. Current researchers have said that hieroglyphics are the most ancient type of writing in the world.
Math
They created the so-called “false position” which was the base or the beginning of what we now know as the algebraic method. They also created the decimal system, complex mathematical formulas, calculated the areas of trapezoids, triangles, and squares, resolved algebraic equations and discovered “Pi”.
Society
The Egyptians were some of the first to incite popular movements, which achieved great things that are remembered throughout history as some of mankind’s greatest historical phenomenon.
Other relevant contributions
- Art and engineering were present in their buildings
- Irrigation canals made the area the biggest grain producer in the ancient world
- The origins of the scientific method can also be dated back to the Egyptians
- The manufacture of glass was used on a daily basis and as an ornament in tombs
- They invented sailing as a mode of transport.
- Alchemy also originated in ancient Egypt.
- They discovered the calendar of 365 and a quarter days, the most scientific calendar of ancient times.
Contributions made by the Mesopotamian culture
Writing
The creation of writing is attributed to the Sumerians around the year 3100 BC. It all began with pictographic writing, which subsequently changed to ideograms, due to the difficulty of drawing the concepts that they wanted to represent. Ideograms made the interpretation of drawings easier. As time went by, ideograms gave way to signs in the form of wedges or spikes that represented sounds. This process of simplification was due to the fact that Mesopotamia wasn’t rich in rocky terrain, which means there was a shortage of stones, but the land was rich in clay, which later allowed them to create bricks. Cuneiform writing was carried out on clay when it was still wet, which would then laid out to dry and baked with other bricks forming larger scriptures.
The Calendar

The Mesopotamian calendar was one of the humankind’s first calendars. Sumerian astronomers were the first to regulate the archaic calendar. The months were divided into four weeks of seven days, in accordance with the phases of the moon, leaving out the last two days of each month, hence the calendar of 12 months and 360 days.
The days of the week were named after the moon, the sun and the five planets that were known by the Sumerians at that time: Mars, Mercury, Jupiter, Venus, and Saturn. These names have evolved in different languages in quite a similar way.
Currency
Before the onset of currency, bartering was the system that people used to exchange products, where they would swap something they didn’t need for something else that they did need. Bartering was used for a long time but the growth of commercial activity came to prove that this system wasn’t practical and hence currency was born.
In Mesopotamia, people began to use bars of gold, silver, copper, iron and bronze to intermediate exchanges but the first two had advantages on the rest due to their shortage, which made them more valuable. Little by little the first coins began to appear to simplify the levying of tax replacing cattle and wheat with coins.
The Wheel
Today’s civilization would not function without the wheel. This circular mechanical object that revolves around an axis is a fundamental component in any machinery, in land vehicles and also to make pottery, despite the fact that the Incas and the Aztecs managed fine without it. The first evidence of the wheel is found in a Sumerian pictogram, dated the year 3500 B.C. One of the first ways it was used was in oxen-pulled wagons to transport goods, as well as lathes to make ceramic objects with greater speed and precision.
The Plow
Given the abundance of water in Mesopotamia, agriculture was one of the most popular jobs. To try and facilitate the task of mixing the soil before planting seeds, the people of Mesopotamia invented and perfected the plow, which is considered an evolution of the pickaxe and the hoe. Initially humans pulled it, but later on animals such as oxen or mules were responsible for pulling the plow.
Plows were made completely out of a single piece of wood and were a similar shape to how they are today, but until the arrival of the Romans, plows did not include iron blades, which allowed them to delve deeper into the earth.
Metallurgy
 Although it is true that metallurgy was invented thousands of years ago, it was in Mesopotamia where copper and copper and bronze to make bronze started being used more regularly. People used copper and bronze in Mesopotamia until bronze finally prevailed.
Although it is true that metallurgy was invented thousands of years ago, it was in Mesopotamia where copper and copper and bronze to make bronze started being used more regularly. People used copper and bronze in Mesopotamia until bronze finally prevailed.
In Mesopotamia, there were three professions related to metallurgy: the qurqurru was in charge of extracting the metal from the ore. The nappahu or smelter would make the pieces of metal from material retrieved from the ore. And finally, the kutimmu would be in charge of manufacturing objects with the precious metals.
The Sexagesimal (base 60) System
The sexagesimal system is a positional numbering system that uses the number 60 as an arithmetic base which facilitates calculations with fractions. The number 60 has the advantage of having many dividers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30 and 60). The sexagesimal system is used to measure times and angles.
First code of laws
Hammurabi was the sixth King of Babylon and is mainly known for the legislation of a new code of laws: the Hammurabi code, which became one the first written laws in history. The Hammurabi code contains 282 laws written on twelve tablets written in Akkadian so that any literate person could read it. These laws provided a punishment for every transgression of the law; punishments that were very tough indeed, such as the death penalty, eye for an eye, disfigurement, and the list goes on.
But apart from the tough punishments, it was the first code of laws that gave the King the opportunity to provide evidence to demonstrate if they were innocent of what they were accused of. Guilty or innocent, there was no in-between. Other Mesopotamian cultures created their own codes of laws such as those of the UrNammu, Esnunna, Lipit-Istar or the Hittite.
Architecture

As I have commented above, due to the lack of rocky terrain, stones were a scarce commodity, which obliged them to make use of mud, manufacturing bricks in order to build thick walls without openings, which meant that their buildings were resistant, heavy and uniform. Wood was also scarce commodity in the region, which is why it wasn’t used in construction work either. Bricks were easy to use, and therefore they were used to build temples, palaces, walls and tombs.
The most characteristic element of Mesopotamia’s temples is the Ziggurat, a square tower with several tiered floors, and on the top of which a sanctuary can be found. Each corner of the tower is orientated towards the four cardinal points, and the floors can be accessed by ramps or stairs located on the sides. These buildings were made with materials such as marble, alabaster, gold and Cedar.
Irrigation
Being surrounded by two rivers, agriculture in Mesopotamia was one of the main ways to stock up on goods. Above we have already mentioned that one of Mesopotamia’s contributions to modern-day culture was the plow to help people work in the field. But in addition to the plow, another important advance in culture was irrigation, better known as riego, in which the correct amount of water is transported in order to help the crops grow. In order to do this, small canals were constructed to transport water from the rivers to the plantations.
Astrology and Astronomy
Assyrian Kings were surrounded by priests and clairvoyants that interpreted dreams and omens based upon astronomical observation. These Kings put the astronomers in charge of finding out the best dates to begin important projects such as the building of temples, and when to start wars…their predictions were also quite accurate.
Priests calculated the length of the days and nights, the sunrises and sunsets, and with this information, they created the first calendar, which has been mentioned above, and with which future eclipses could be predicted. The predictions were based upon the Moon’s positioning in the sky but also in particular during the appearance of the first half Moon at the start of each month. These predictions were not applied to individuals, but instead were used to predict the future of crops, wars or epidemics.
Contributions made by the Indian Civilization
The main advance of the Ancient Indian civilization was its urban architecture; their buildings were made of adobe bricks, had several floors and an efficient sewage system. They were also the first to cultivate and make cotton fabrics.
Later on, in the 5th Century, when India was a part of the Gupta empire, they made big innovations:
Math
 They developed the decimal system, which established the numeric symbols that we use today. They were the first, along with the Mayas, to invent the concept of zero. The mathematician and astronomer Aryabhata determined the value of “Pi” (the approximate relation between the circumference and diameter of a circle) and the spherical shape and rotation of the Earth. Other astronomers calculated the diameter of the Muna and wrote about gravitation.
They developed the decimal system, which established the numeric symbols that we use today. They were the first, along with the Mayas, to invent the concept of zero. The mathematician and astronomer Aryabhata determined the value of “Pi” (the approximate relation between the circumference and diameter of a circle) and the spherical shape and rotation of the Earth. Other astronomers calculated the diameter of the Muna and wrote about gravitation.
Metallurgy: they produced steel to make weapons and armors.
Medicine: they knew how to sterilize and how to use drugs to treat the sick. They cured bites from poisonous snakes. They did surgery such as gallbladder extraction and intestinal stitching.
Contributions made by the Chinese Civilization
The great contributions of the Ancient Chinese culture which are appreciated to this day can be separated into three areas:
Arts
They created pagodas, which were basically roofs which overlapped each other. They also manufactured porcelain and silk items which linked them to the spiritual world they believed in.
They are known as the first culture to use ink in writing. They also used paper made from bamboo fibers, tree bark, and water.
Another of their longest-lasting inventions, alongside the previous two, was gunpowder, which comes from mixing nitrate, charcoal with other substances. It was used to make fireworks.
Sciences
There were major inventions, some of the most important of which being the first compass and the first seismograph.
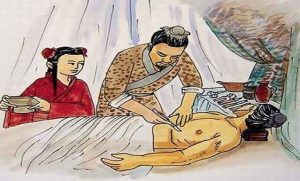
In medicine, they tried to make sure the human body was in harmony with the mind, the spirit, and with its environment, the Tao, which is the origin of the universe. It has two primordial forces which have an unstable balance: Yin and Yang. This cosmology defines illnesses as a rupture in naural balance and to treat them, balance must be returned. Harmony can be restored with accupuncture which consists of applying needles to 365 points; when the needles are inserted into these points, the Yin and Yang in the body are stabilized. In the Golden Age of Taoism, they began to approach the use of vegetable and mineral remedies, poisons, respiratory techniques and physical exercise.
With regards to literature, many texts were created. An example is the “Book of Origins”, which tells the story of the Zhou dynasty; in this book, its author Tchouang Tseu, who lived in the 3 rd Century BC, structured the main doctrines of Taoism. The Confucianists also wrote their main doctrines in “The Invariable Average” and in “The Great Study“.
Architecture
Their main principles were aesthetic beauty and functionality. Their houses, for example, were made from wood whilst the roofs had curved eaves and the roof tiles were painted in different colors. Their great creations include the Great Wall of China and the Terracotta Army.
The Great Wall of China: Built and rebuilt between the 5 th Century B.C. and the 17th Century A.D., its purpose was to protect the Northern area of the Chinese Empire during the dynasties of the attacks of the Xiongu nomads from Mongolia and Manchuria. It is approximately 8851.8 kilometers long, and goes from the Korean border to the Gobi desert, it is between 6 and 7 meters high and 4 to 5 meters wide, and was built by more than a million warriors. It is also known for being the world’s biggest cemetery due to the fact that around 10 million workers died during its construction. It has been named one of the Seven Wonders of the Modern World.
Cultural contributions of the Greek civilization
The Ancient Greeks developed independent cities (called Polis), which encouraged them to be strongly independent, but also promoted a strong appreciation for mankind, who developed them and accomplished many things, which became a real legacy for the Western world. Among them are the following:
Art

In this activity, the Greek concept of “nothing in excess” was practiced, seen for example in architecture where there were no large monumental buildings, but instead a series of public buildings linked to daily life in the cities. In these constructions, the use of columns with different styles was common (Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian).
Sculpture also has a prominent place in Greek culture, and in their sculptures, the Greeks show their appreciation for the human being, who is usually represented naked and harmonious in its anatomical composition. Phidias and Miron are among the leading sculptors of the Greek world.
Philosophy
The “love of wisdom” began with the Greeks, as can be seen in their search for the ground substances that the Universe is composed of (for example, for Tales it was water, however for Anaximenes it was air)
During the classic period, philosophers reflected upon the nature of man (anthropological period), of whom some of the most notable figures are Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle.
Socrates proposed that one must know oneself in order to be more wise and virtuous. He was accused of corrupting the youth, so he was condemned to drink hemlock. Plato was a disciple of the philosophers mentioned above (in fact information that we know about Socrates was found through Platonic dialogues). He suggested that there is a series of ideal elements that should govern man’s conduct.
Aristotle was one of Plato’s disciples, but unlike his teacher, he was a realist, not an idealist. He devoted himself to study a number of subjects, amongst them logic, metaphysics, politics, and biology.
Theatre
This activity emerged in the Greek classical period and is closely linked to the religious festivities in honor of the God Dionysus (God of wine and festivities). In these events, done outdoors, they performed tragedies, which were tense plays with a tragic denouement. Authors such as Sophocles (author of “Oedipus Rex”), Aeschylus (author of the “Oresteia”) and Euripides (author of “The Bacchae”) were particularly renowned. Comedies also had an important role, as they satirized Greek society and politics, conveying the opposite message of a tragedy. Aristophanes (author of “The Birds”, where the imperialism of Athens was critiqued) particularly stands out in this type of theater.
Sciences
While the Greeks, in some areas, were not creators, they did focus on establishing some theorems, such as Pythagoras in mathematics. Medicine emerged in Greece because Hippocrates believed that illnesses were caused by natural causes, and not through magical practices.
History also has a leading role in Greece, where the research side was developed, it no longer being seen as a simple account of events. Its major exponents were Herodotus and Thucydides.
Democracy

As explained above, the main political contribution to the Western world was the development of the democratic system in the polis of Athens. According to Pericles, who is considered the leading exponent of this regime, in Athens…
“We benefit from a political regime that does not imitate the laws of our neighboring states; we do more than imitate others, on the contrary, we serve as a model to others. This regimen has been named democracy because the administration is in the hands, not of a few, but of the majority. In the settling of private disputes, everyone is equal before the law. Election to public office is made on the basis of availability, not on the basis of membership to a particular class. No man is kept out of public office by the obscurity of his social standing because of his poverty, as long as he wishes to serve the state.”
(Summary of the funeral speech of Pericles in honor of the fallen in the Wars of the Peloponnese. In Thucydides, the Peloponnesian War)
The Olympic Games
The Games were considered the most important religious holiday in the Greek world, where representatives from different cities would gather to compete in races, fights, discus throwing, and other games. Despite the fact that they have changed a lot over time, they originate in the Greek civilization.
Contributions made by the Roman Civilization
The main contributions that the Ancient Roman Empire brought to us were: architecture, sculpture, technique, painting and contributions to civilization from Rome. Also, Latin, their mother tongue, left a legacy to humanity.
Architecture
The Romans constructed buildings with arches, domes, and vaults, which they adopted from the Etruscans, mixing these elements with some decorative elements of Greek architecture.
Roman architecture is characterized by its monumental quality and by the way their buildings were open to the public. Rome and the Empire were filled with circuses, theaters, amphitheaters, baths, roads, forums, basilicas, arches, and more.
For the Romans, decoration and hygiene were very important, which is why they built squares, forums, markets, public baths, aqueducts, viaducts, bridges, and sewerage systems, whose remains can still be found in the rest of Europe.
Rome’s main Amphitheater was the Roman Colisseum

The Roman Colosseum is a huge amphitheater, which was built to give favors to the best and most legendary wrestlers, as well as to celebrate the glory of the Roman Empire. The Colosseum is located in the heart of Rome. Its interior is made from sand-covered wood, and underneath there is a maze of halls divided into several floors, where dungeons and animal cages were kept. Cavea, the grandstand area, and was divided into three overlapping sectors, with a wooden fourth level for the standing spectators. Each sector was reserved for a different social class. In the tallest part, the Colosseum has a Velarium; a large tent that protected the spectators from the sun. The Emperor and the most important members of Roman society would sit at the podium.
Sculpture
Emperors and Roman generals built arches and columns to celebrate the memory of their triumphs, which they decorated beautifully with embossments and statues to remember their feats.
During the Republic, the severity of the Etruscan tradition still prevailed in Roman sculpture. The Romans tried to imitate the artistic forms of Greece and Asia Minor in their statues, paintings, and works of art.
Painting
Roman painting is distinguishable by the frescoes that decorated the houses in Pompeii and some tombs. Their painting style isn’t just a simple imitation of Greek painting; it has a uniqueness that is incomparable to any other style.
Mosaic, or decoration with glazed bricks, originated from the East and was commonly used in Rome and throughout the whole Empire. It was used to represent big and important scenes with a technique similar to that used in painting.
Technology
Pure science wasn’t cultivated in Rome; however, technology was advanced, as it was practical and useful.
Their enormous constructions, extensive walkways, bridges and aqueducts, and walls are testimony of their extensive knowledge of architecture, metallurgy, and hydraulics.
Aqueducts
 Rome had seven hills and eleven aqueducts. The size of the city grew proportionally with the water that entered it. When the barbarians cut the water supply, Rome fell.
Rome had seven hills and eleven aqueducts. The size of the city grew proportionally with the water that entered it. When the barbarians cut the water supply, Rome fell.
In parts of the city, it is still possible to see remains of gigantic arcs, grand works of engineering. The grandeur of Rome is also apparent in the remains of the aqueducts in the southeast of Rome.
Aqueducts were canals built from waterproof cement and were covered with slabs of stone. They transported the water that collected at the bottom of the hills to the city, flowing at a constant angle. The water gathered pressure and was stored in large tanks next to the spring.
When the water reached the center of Rome it was used to supply fountains and public buildings. The Romans spent a large part of their public funds ensuring that the facilities were well maintained so that there was always a supply of clean and fresh water.
In Rome’s heyday, there was always a large supply of clean and fresh water; however during the sieges of the barbarians they suffered from frequent water supply cut-offs until it finally dried up.
Latin: The origin of the Romance languages
When the Romans conquered new regions, they imposed their own language, Latin. However, it was not “pure” Latin, but common or “Vulgar” Latin, which was what was spoken at home, in the street and in the field.
Latin and Romance languages evolved from Vulgar Latin, what we know today as Portuguese, Catalan, Provençal, French, Sardinian, Italian, Romansh, Romanian and Spanish or Castilian. All places where the Latin language was spoken were called “Romania”; this included five European Nations: Portugal, Spain, France, Italy and Romania. Latin had an enormous influence.
Other contributions to modern civilization
- The Roman law, made up of original laws of the Republic, Imperial rights, and decisions made in courts were all collected in the “Code of Justinian”, which was used as the basis for the famous Napoleonic Code.
- The Roman peace that was maintained in the ancient world for 200 years.
- The public buildings that the Romans built for the whole population to use.
- Literature and Roman history, classical Latin works and work compiled by historians have served as a model and an important source of knowledge.
- Politics. Despite the mistakes made in civil wars and the failure of their economic system, which was based on slavery and estates, Roman politics still forms a base for modern nations.
Contributions made by the Aztec Civilization
The Aztecs stood out for their ability to build cities, their knowledge of science and their varied ways of artistic expression.
They had their own hieroglyphic writing, a numeration system and a calendar that consisted of 18 months of 20 days each with 5 extra days, but it was inferior to the Mayan calendar.

They developed metallurgy skills, working specifically with gold and copper.
They made cotton dresses.
Their ceramics were distinguished by the sets of polychromatic vases.
Chewing gum was another important contribution that the Aztecs brought to the world.
They were the first to chew the sap that was secreted by the rubber tree.
We can thank the Aztecs for bringing the flavors of vanilla and chocolate to the world.
Chinampas were an ingenious Mexican invention and are an example of the advanced level of technological and agricultural advancement that the Aztecs achieved. They are just a small part of the striking ecological and hydraulic balance that was around in the great Tenochtitlan until before the Spanish conquest.
Chinampas were true floating gardens, and were attached to the subsoil, nailing stakes or tree trunks, which gave stability to the ground when they took root.
Between the chinampas there were canals that were used as a quick communication route, which substituted the absence of the wheel.
In Xochimilco these Mexican wonders can still be found.
The Aztec codices, like the majority of the pre-Cortesian codices, were made with a special paper made from bark from the amatl tree.
Cultivation techniques
- Seed selection
- Crop rotation
- Selection of land that is suitable for cultivation
- Selection of the time of year
- Taking the rain and the phases of the moon into account
- These are the same techniques that farmers use today.
- The cultivation of maize, which was used to make:
- Bread
- Cake
- Tortillas
- Chicha (a fermented drink)
- These are foods that we often find in our daily diet and drinks that many farmers still enjoy.
Astronomy
Based on the cycles of the Sun or Venus they put together a solar calendar that they called the Sun Stone, which represented the 5 ages of humanity.
Art and Architecture
The State helped a large number of specialized artisans to develop feather art and precious metalwork.
They built several important constructions such as the Teocalli.
Language and Writing
The language spoken in the Empire was called Nahuatl.
Writing was based upon symbols that described history and mythology.
Contributions made by the Mayan Civilization
Astronomy

The Mayans developed a calendar that is as precise as the one we use today.
According to the observation of the Sun, the Moon, and the stars, they could predict phenomena such as eclipses and equinoxes.
Math
They were aware of the concept of zero and used it long before was discovered in other places.
They used a vigesimal number system, multiplying by 20 instead of 10.
Architecture
They built great monuments such as Kukulkan in Chichen-itza.
They built the Korbel Arch (the false arch), which replaced the real one.


